What was the first space technology? In a world where space exploration has become synonymous with innovation and human achievement, understanding the roots of space technology offers us a glimpse into humanity’s relentless pursuit of the unknown. From the earliest attempts to reach beyond our atmosphere to today’s sophisticated spacecraft, space technology has played a crucial role in expanding our understanding of the universe and enhancing our everyday lives.
But where did it all begin? What was the first space technology that set humanity on this celestial journey? This article dives deep into the fascinating history of space technology, tracing its origins and exploring how it has evolved over the years.

The Dawn of Space Exploration
Space exploration didn’t just happen overnight; it was the result of centuries of scientific advancements and visionary thinkers who dared to dream beyond the confines of Earth. The journey began with astronomers like Nicolaus Copernicus and Galileo Galilei, whose work laid the groundwork for understanding our place in the cosmos.
By the 17th century, Sir Isaac Newton’s laws of motion and universal gravitation provided a theoretical foundation that would eventually make space travel possible. These early scientific advancements were crucial in igniting the curiosity and ambition that would later drive humanity to explore the stars.
The Birth of Rocketry
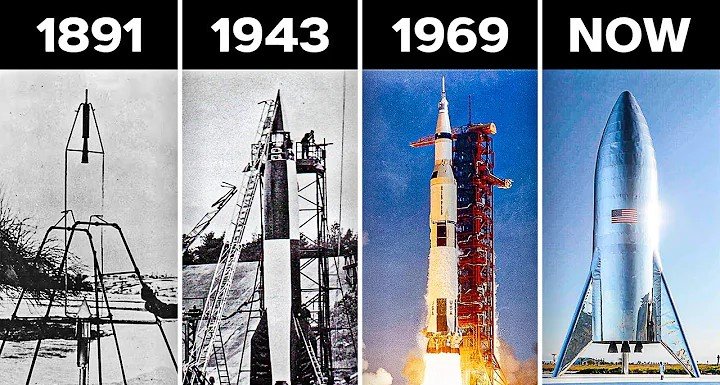
Rocketry, as we know it today, is deeply rooted in ancient history. The invention of gunpowder in 9th-century China paved the way for the first rudimentary rockets, which were primarily used for military purposes. These early rockets were nothing more than simple tubes filled with gunpowder that, when ignited, propelled themselves forward with a fiery thrust.
The concept of using rockets for exploration began to take shape in the 20th century, thanks to pioneering figures like Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, who is often regarded as the “father of astronautics.” Tsiolkovsky’s visionary ideas about space travel and the use of liquid propellants laid the groundwork for future innovations in rocketry.
Robert H. Goddard: The Father of Modern Rocketry
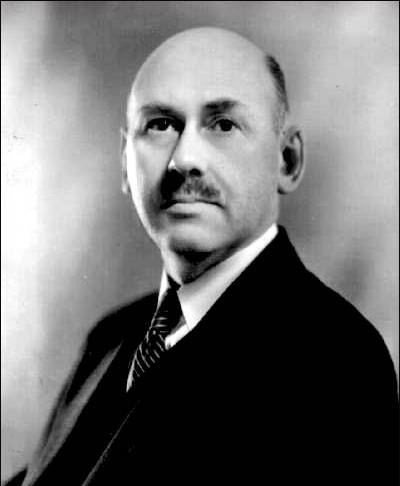

No discussion about the origins of space technology would be complete without mentioning Robert H. Goddard, an American physicist and engineer who is widely credited with creating the first liquid-fueled rocket. Born in 1882, Goddard’s fascination with space began at a young age, inspired by the works of science fiction writers like H.G. Wells.
Goddard’s groundbreaking work in rocketry was driven by a deep-seated belief in the potential of space exploration. In 1926, he successfully launched the world’s first liquid-fueled rocket in Auburn, Massachusetts, reaching an altitude of 41 feet and demonstrating the viability of liquid propulsion systems. His pioneering efforts earned him the title of the “father of modern rocketry,” and his inventions laid the foundation for future developments in space technology.
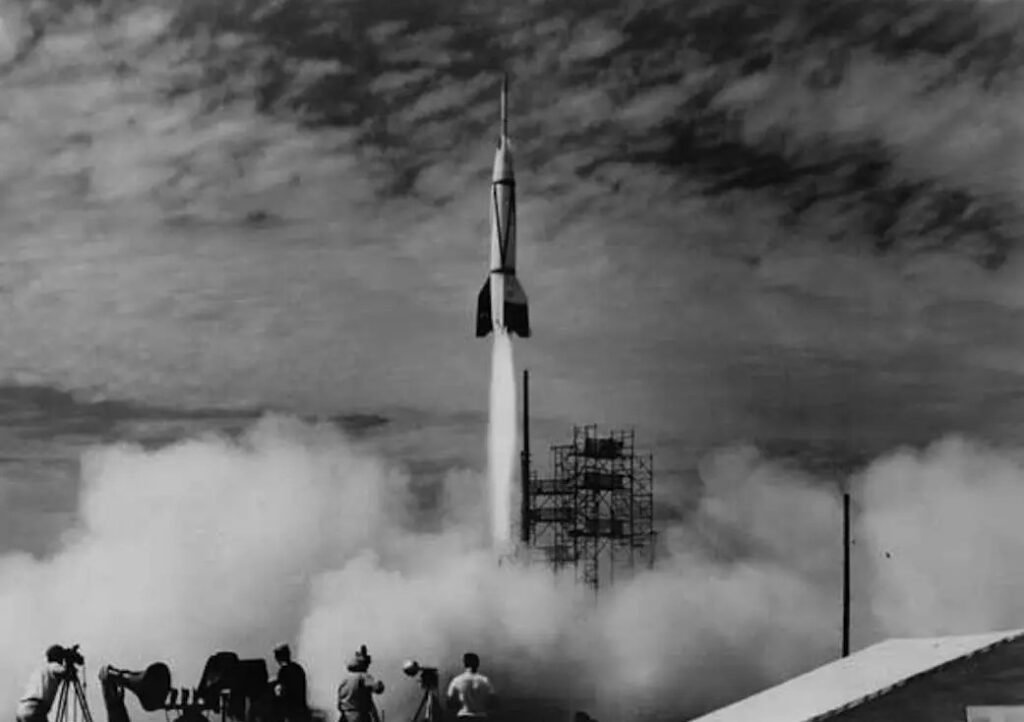
The V-2 Rocket: A Milestone in Rocket Technology
While Goddard was making strides in America, the development of the V-2 rocket in Nazi Germany marked a significant milestone in rocket technology. Designed by Wernher von Braun and his team, the V-2 was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile and became the prototype for modern rockets.

Launched in 1944, the V-2 reached altitudes of 100 miles and speeds of 3,500 miles per hour, making it the first man-made object to reach the edge of space. Although it was developed for military purposes, the V-2’s technological advancements had a profound impact on post-war space exploration efforts, as scientists on both sides of the Atlantic recognized its potential for peaceful applications.
The Space Race: Ushering a New Era
The Cold War era brought about a fierce competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, known as the Space Race. This rivalry was fueled by political tensions and a desire for technological supremacy, leading to unprecedented advancements in space technology.
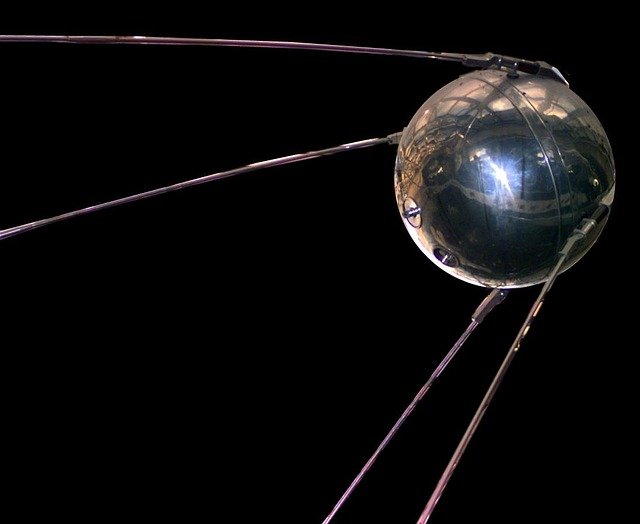
The Space Race saw numerous milestones that would shape the future of space exploration. In 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, the world’s first artificial satellite, sparking a global frenzy and marking the beginning of the space age. This achievement not only demonstrated the Soviet Union’s technological prowess but also highlighted the strategic importance of space technology in the modern world.
Sputnik: The First Artificial Satellite
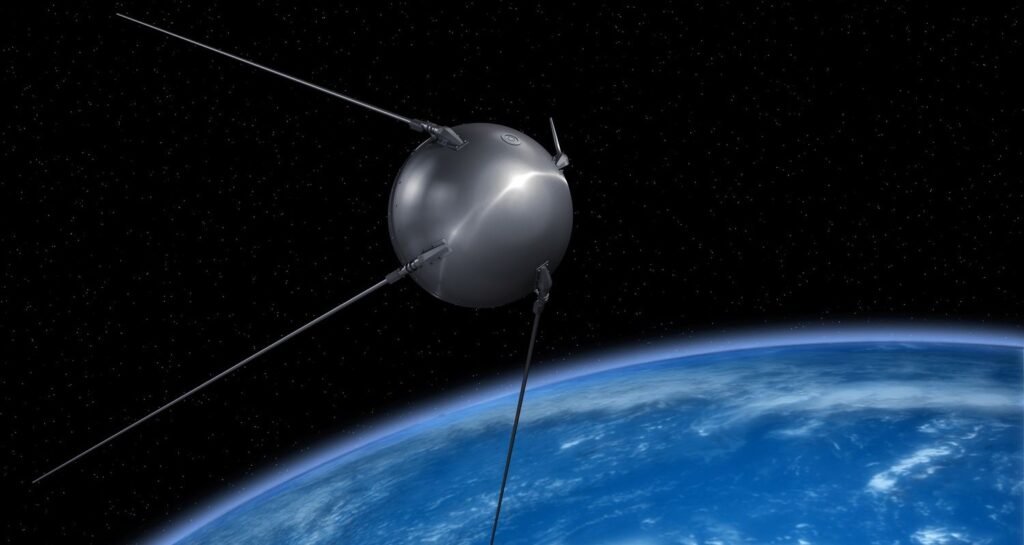
Sputnik 1’s launch on October 4, 1957, was a watershed moment in the history of space technology. Weighing just 184 pounds, this spherical satellite orbited the Earth and transmitted radio signals back to ground stations. Its success sent shockwaves across the globe, prompting nations to accelerate their own space programs.
The implications of Sputnik’s launch were profound, as it marked the first time humanity had placed an object in orbit around the Earth. This achievement opened the door to future space exploration missions and underscored the potential of satellites for communication, weather monitoring, and scientific research.
What was the first space technology? The Role of NASA in Space Exploration
In response to the Soviet Union’s early successes, the United States established the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1958. NASA quickly became a driving force in space exploration, spearheading a series of ambitious missions aimed at advancing human understanding of the cosmos.
NASA’s early achievements included the Mercury and Gemini programs, which laid the groundwork for human spaceflight and tested the capabilities needed for lunar exploration. These programs paved the way for the Apollo program, which would become one of the most significant endeavors in the history of space exploration.
The Apollo Program: A Giant Leap for Mankind
The Apollo program stands as a testament to human ingenuity and determination. Launched in the 1960s, its primary goal was to land a man on the Moon and return him safely to Earth. This ambitious mission was driven by President John F. Kennedy’s vision of reaching the Moon before the end of the decade.
On July 20, 1969, the world watched in awe as Apollo 11’s lunar module, Eagle, touched down on the Moon’s surface. Astronaut Neil Armstrong’s historic words, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind,” echoed across the globe, symbolizing the culmination of years of technological innovation and human effort.
The Apollo program not only achieved its goal of landing astronauts on the Moon but also advanced our understanding of space travel, paving the way for future exploration and scientific discoveries.
Space Technology in the Modern Era
Since the Apollo program, space technology has continued to evolve at a rapid pace, pushing the boundaries of what was once thought possible. The development of the Space Shuttle program in the 1980s marked a new era in space travel, with reusable spacecraft capable of carrying astronauts
and payloads into orbit.
In recent years, the International Space Station (ISS) has become a symbol of international collaboration and a testament to human achievement. Orbiting 250 miles above Earth, the ISS serves as a microgravity laboratory where scientists conduct experiments that advance our understanding of biology, physics, and astronomy.
Private Sector Involvement in Space Exploration
In the 21st century, the private sector has emerged as a key player in space exploration, revolutionizing the industry with new technologies and innovative approaches. Companies like SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, have made significant strides in reducing the cost of space travel and increasing accessibility.
SpaceX’s Falcon 1, launched in 2008, was the first privately developed liquid-fueled rocket to reach orbit. Since then, the company has achieved numerous milestones, including the successful launch and landing of reusable rockets, paving the way for more sustainable space travel.
Other private companies, such as Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, are also making significant contributions to space exploration, with ambitious plans for commercial space travel and lunar missions. This surge in private sector involvement has democratized access to space technology, opening new possibilities for exploration and discovery.
Current Trends in Space Technology
The rapid pace of technological advancements continues to reshape the landscape of space exploration. Recent innovations, such as miniaturized satellites and advanced propulsion systems, have enabled more efficient and cost-effective missions.
CubeSats, small satellites often no larger than a shoebox, have become increasingly popular due to their versatility and affordability. These compact satellites are used for a wide range of applications, from Earth observation to scientific research, and have expanded the capabilities of space missions.
Additionally, the development of ion propulsion systems and nuclear thermal propulsion holds the potential to revolutionize space travel by providing faster and more efficient means of reaching distant destinations. These technologies promise to unlock new frontiers and enable missions that were once deemed impractical.
The Future of Space Exploration
As we look to the future, the possibilities for space exploration seem limitless. With plans for crewed missions to Mars, the establishment of lunar colonies, and the exploration of asteroids, humanity stands on the brink of a new era of discovery.
International collaboration will play a crucial role in advancing space technology and overcoming the challenges of deep-space exploration. Initiatives like the Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence, exemplify the importance of global partnerships in achieving ambitious goals.
The Impact of Space Technology on Everyday Life
Beyond its contributions to scientific discovery, space technology has had a profound impact on our daily lives. From the development of satellite-based communication systems to advancements in weather forecasting and navigation, space technology has revolutionized the way we live and work.
The Global Positioning System (GPS), a network of satellites orbiting the Earth, has become an integral part of modern life, enabling everything from precise navigation to financial transactions. Similarly, satellite imagery plays a vital role in monitoring climate change, managing natural resources, and responding to disasters.
Moreover, innovations derived from space technology have found applications in various industries, including healthcare, agriculture, and transportation. From medical imaging devices to precision farming techniques, the benefits of space technology extend far beyond the boundaries of space exploration.
Conclusion
The journey of space technology from its humble beginnings to the present day is a testament to humanity’s insatiable curiosity and determination to explore the unknown. From the earliest rockets to the cutting-edge spacecraft of today, space technology has propelled us into a new era of discovery and innovation.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, space technology will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of exploration, scientific research, and everyday life. By understanding the origins of space technology, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable achievements that have paved the way for humanity’s journey into the cosmos.
FAQs
- What were the earliest forms of space technology?
- The earliest forms of space technology date back to ancient China, where gunpowder-powered rockets were used for military purposes. However, the modern era of space technology began with the development of liquid-fueled rockets by pioneers like Robert H. Goddard.
- How did the V-2 Rocket influence modern space exploration?
- The V-2 rocket, developed during World War II, was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile and marked a significant milestone in rocket technology. Its design and technological advancements laid the groundwork for post-war space exploration efforts and influenced the development of future rockets.
- What was the significance of the Apollo program?
- The Apollo program was a pivotal moment in space exploration, achieving the first successful manned missions to the Moon. The program advanced our understanding of space travel, provided valuable scientific data, and inspired generations of scientists and engineers to pursue careers in space exploration.
- How is space technology being used today?
- Space technology is used in various applications today, from satellite-based communication systems and GPS navigation to weather forecasting and scientific research. It also plays a crucial role in industries such as agriculture, healthcare, and transportation, driving innovation and improving quality of life.
- What does the future hold for space exploration?
- The future of space exploration is filled with exciting possibilities, including crewed missions to Mars, the establishment of lunar colonies, and the exploration of distant celestial bodies. Advances in propulsion systems, international collaboration, and private sector involvement will continue to shape the future of space exploration.

