What is inside the black hole? There are two components to black holes. There is the event horizon, which is essentially the point at which gravity becomes too great for anything to escape. You can think of it as the surface. The singularity then sits at the center. That’s the term we use to characterize an indefinitely dense and small point.
Black holes are some of the most fascinating and mysterious objects in the universe. Their very nature challenges our understanding of physics, particularly when it comes to answering the question: “What is inside a black hole?” Let’s delve into this intriguing topic and explore what lies beyond the event horizon.
Understanding Black Holes
Definition and Formation
A black hole is a region in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from it. They form from the remnants of massive stars that have undergone a supernova explosion, collapsing under their own gravity. There are also supermassive black holes found at the centers of galaxies, whose origins are still being investigated.
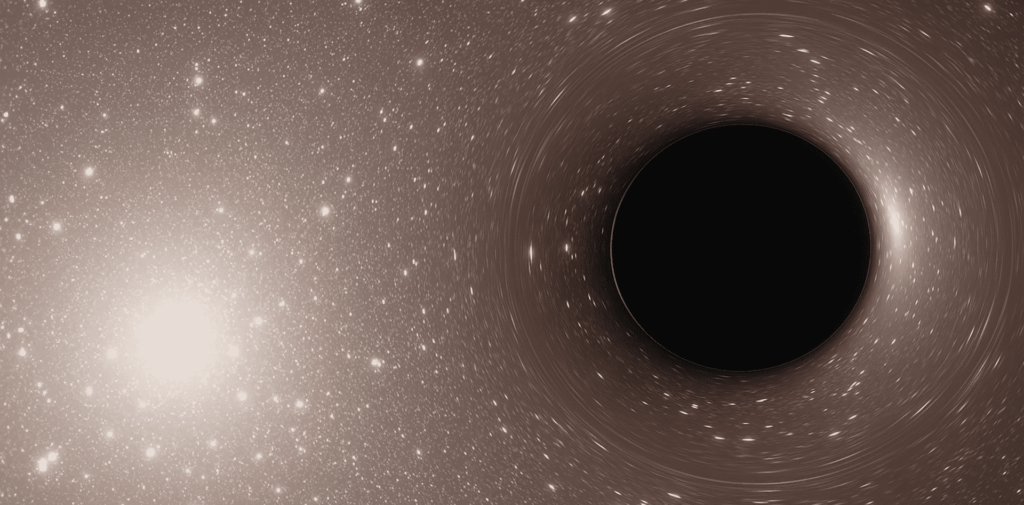
What is inside the black hole? Event Horizon
The event horizon is the boundary surrounding a black hole. It marks the point beyond which nothing can escape the black hole’s gravitational pull. For an outside observer, objects approaching the event horizon appear to slow down and fade away, due to the extreme warping of space and time.
The Concept of Singularity
What is Singularity?
At the center of a black hole lies a singularity, a point where the density of matter becomes infinitely large and the gravitational forces are infinitely strong. This is where our current understanding of physics breaks down. Singularities represent the limits of our knowledge and challenge the boundaries of physical laws.
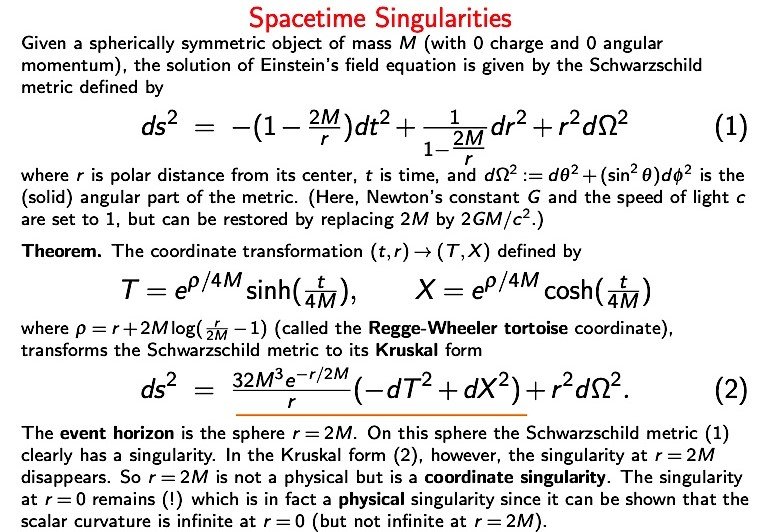
Mathematical and Physical Singularity
Mathematically, a singularity is a point where certain quantities become infinite. Physically, it signifies a breakdown in the laws of physics. For example, in black holes, the equations of general relativity predict infinite density, which implies that traditional concepts of space and time no longer apply.
Theoretical Models of the Interior
General Relativity
According to general relativity, the interior of a black hole is characterized by a singularity surrounded by the event horizon. Einstein’s theory describes how gravity causes space-time to curve, leading to the formation of a black hole. However, general relativity alone cannot fully explain the interior of black holes, as it breaks down at the singularity.
Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics introduces the idea that quantum effects could modify our understanding of singularities. Quantum effects might suggest that the singularity is not a point but rather a region where quantum gravitational effects come into play. This could potentially resolve some of the infinities predicted by general relativity.
What Happens at the Event Horizon?
Time Dilation
Time dilation near a black hole’s event horizon causes time to appear to slow down relative to an outside observer. As an object approaches the event horizon, it seems to slow down and never actually crosses the boundary from the perspective of a distant observer.
Spaghettification
The process known as spaghettification occurs when objects are stretched into long, thin shapes as they approach a black hole. This happens because the gravitational forces vary greatly across an object, creating a tidal effect that elongates and compresses it.
Inside the Black Hole
What We Know
Currently, our knowledge about the interior of black holes comes from theoretical models and observational evidence. We infer their properties based on how they affect nearby matter and emit radiation. However, direct observation of the interior is beyond our current technological capabilities.
Theories and Hypotheses
Various theories and hypotheses attempt to describe what happens inside a black hole. Some suggest that the singularity might be a region of extremely high density, while others propose that the interior could be connected to other regions of space-time, possibly even other universes.
Exploring the Unknown
Current Research
Current research involves studying black holes through indirect means, such as observing the behavior of matter around them and detecting gravitational waves. Upcoming missions and technologies may offer new insights into the nature of black holes.
Future Prospects
Future prospects include advanced observational techniques and theoretical models that could provide more information about black hole interiors. The development of technologies like the Event Horizon Telescope and space-based gravitational wave detectors may bring us closer to understanding these enigmatic objects.
Implications for Physics
Impact on Our Understanding
The study of black holes challenges our understanding of fundamental physics. It highlights the need for new theories that can reconcile general relativity with quantum mechanics and provide a comprehensive description of the universe’s most extreme conditions.
Potential Discoveries
Potential discoveries in black hole research could lead to breakthroughs in our understanding of gravity, space-time, and the fundamental nature of reality. These discoveries might reshape our view of the universe and lead to new advancements in physics.
Conclusion
Understanding what is inside a black hole remains one of the most intriguing questions in modern science. While we have made significant strides in studying black holes, much remains unknown. Continued research and technological advancements will be crucial in uncovering the mysteries of these cosmic giants.
FAQs
- What is a singularity in a black hole?
- A singularity is a point within a black hole where density becomes infinitely large and the laws of physics break down.
- How does the event horizon affect our observation of black holes?
- The event horizon is the boundary beyond which nothing can escape the black hole’s gravitational pull, making direct observation impossible.
- What is spaghettification?
- Spaghettification is the process where objects are stretched and compressed into long, thin shapes due to extreme gravitational forces near a black hole.
- Can we directly observe the inside of a black hole?
- No, direct observation is currently impossible due to the extreme conditions and the event horizon that prevents light from escaping.
- What future technologies might help us understand black holes better?
- Future technologies such as advanced gravitational wave detectors and space-based observatories may provide new insights into black hole interiors.

