Do you want to know the Trip to the moon cost? The cost to go to the moon varies significantly, but estimates range from $140 billion for the first nine trips to around $175 million per seat for a trip around the moon with private companies. The moon has always captured humanity’s imagination, serving as a beacon for explorers and dreamers alike. With advancements in space technology, the prospect of lunar travel is transitioning from a distant dream to an imminent reality. A new era of space exploration beckons, with several companies at the forefront, each with their ambitions to ferry humans and cargo across the expanse to our celestial neighbor.

SpaceX: Pioneering Deep Space Travel
SpaceX, led by visionary Elon Musk, is no stranger to the space industry’s limelight. With its groundbreaking reusable rockets, SpaceX has revolutionized how we approach space travel, making it more cost-effective and sustainable. The jewel in SpaceX’s crown, the Starship spacecraft, is designed for versatility and capability, poised to offer lunar trips that promise not only to carry large cargo but also to transport crew to the moon’s surface.
Key Characteristics:
- Payload Capacity: Leading the pack, capable of carrying significant cargo along with crew members.
- Affordability: Though specific pricing is speculative, SpaceX aims to make space travel more accessible through reusable technology.
- Schedule Reliability: Building on its track record of successful missions, SpaceX demonstrates steady progress toward lunar missions.
Blue Origin: Opening Space for All
Founded by Jeff Bezos, Blue Origin’s vision encapsulates enabling a future where millions of people live and work in space. While its primary focus has been on suborbital flight experiences, their ambitions extend far beyond. With the Blue Moon lander, Blue Origin plans to cater to space tourism by offering highly specialized lunar lander services that could deliver large payloads to the moon’s surface, paving the way for sustained human presence and activity.
Key Characteristics:
- Service Focus: Although still in the planning phase, Blue Origin positions itself strongly in space tourism with potential crewed lunar landings.
- Innovation: The Blue Moon lander represents a significant leap forward, designed to deliver both rovers and other scientific payloads.
- Future Potential: Blue Origin’s vision includes developing infrastructures to support lunar settlement and beyond.
Astrobotic: The Commercial Gateway to the Moon
Astrobotic stands out for its focus on payload delivery, working closely with NASA and other clients to ferry scientific and commercial payloads to the lunar surface. With its Peregrine lander, Astrobotic is at the forefront of offering accessible lunar payload services, marking a vital step towards broader lunar exploration. While initially concentrating on uncrewed missions, Astrobotic has aspirations for crewed missions, making space more accessible to everyone.
Key Characteristics:
- Specialization: Expertise in lunar payload delivery, providing a crucial service for scientific and commercial exploration.
- Partnerships: Strong collaboration with NASA underlines its credibility and reliability as a service provider.
- Crewed Mission Plans: Looking ahead, Astrobotic aims to extend its services to include human passengers, broadening the scope of lunar exploration.
Trip to the moon cost: Comparison and Future Outlook
When comparing these pioneers, SpaceX leads in payload capabilities and is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with crewed lunar travel. Blue Origin, with its focus on space tourism, promises to make the moon more accessible to private individuals, aspiring to blend exploration with leisure. Astrobotic, while more niche, plays a critical role in laying the groundwork for sustained lunar operations through its delivery services.
The future of lunar travel hinges on the combined efforts of these innovators. With each company carving its path to the moon, the dream of lunar exploration becomes increasingly tangible. Affordability, payload capacity, and schedule reliability remain key factors as these entities stride towards making lunar travel a routine reality. The next few years promise to be a defining era in human space exploration, with the moon merely the first step in the broader voyage into the cosmos.
Embarking on a Journey to the Moon: An In-depth Cost and Booking Guide
Ever dreamed of walking where only a dozen have dared to venture? A lunar adventure has transcended from science fiction fantasies into a tangible reality for a select few. For aspiring astronauts, the lure of the moon’s desolate beauty is undeniable, but the complexity and costs involved can be daunting. Here’s what you need to know about the financial, procedural, and legal aspects of booking a trip to the moon.
Detailed Cost Breakdown
Initial Reservation Deposit: A leap towards the moon begins with a substantial non-refundable deposit, anchoring your commitment and securing a coveted seat aboard a spacecraft.
Training Costs: Space doesn’t forgive the unprepared. Extensive training is essential, ensuring you’re equipped to handle space travel’s physical and psychological demands.
Launch and Return Costs: This includes everything from the rocket fuel igniting your departure from Earth to the intricate operations ensuring your safe re-entry into our planet’s atmosphere.
Spacecraft Accommodation: Beyond mere transport, your spacecraft is your temporary home. Accommodation costs encompass your essentials—food, water, and breathable air—for the duration of your voyage.
Personal Space Gear: Customized space suits and specialized equipment aren’t just for show; they’re crucial for your safety and the success of your lunar exploration.
Insurance: Space is the ultimate unknown. Specialized travel insurance mitigates the financial risk of the unforeseeable, covering everything from medical emergencies to loss of personal items.
Additional Services: For those wanting to immortalize their experience, options range from personalized souvenirs to professional photography services, each adding a unique touch to your adventure.
Booking Steps
- Initial Inquiry: Your first small step involves reaching out to a space travel agency renowned for its lunar expeditions.
- Consultation and Selection: In-depth discussions help tailor your lunar adventure to your dreams, considering everything from launch windows to your budget’s constraints.
- Reservation Deposit: Solidify your intentions by placing a non-refundable deposit, a gateway to securing your spot among the stars.
- Training Registration: Embark on the rigorous yet rewarding training program designed to prepare you physically and mentally for the challenges of space.
- Final Payment: With training under your belt and departure dates drawing close, the remaining balance of your trip cost is due.
- Gear Fitting and Packing: A fitting session ensures your space suit is as ready for the moon as you are. Concurrently, you’ll be advised on how to pack for this unprecedented voyage.
- Launch Preparation: In the final days before departure, you’ll undergo health checks, gear checks, and briefings, ensuring you’re fully prepared for the monumental journey ahead.
Legal and Liability Considerations
- Explicit Waivers: To proceed, you must acknowledge space travel’s inherent risks, releasing affiliates from liability for personal harm or property damage.
- Insurance Coverage: Understand the full scope of your specialized insurance, including limitations and responsibilities, ensuring you’re adequately covered for every eventuality.
- Refund and Cancellation Policies: Familiarize yourself with the conditions under which deposits and payments are forfeited. Transparency here is key to navigating potential unforeseen obstacles.
- Safety Responsibility: A delineation of safety responsibilities is crucial. Adhering to guidelines and protocols maximizes your safety and the overall success of the mission.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assurance that all operational facets of your lunar trip are in strict adherence with relevant space and aviation regulations protects all parties involved.
A trip to the moon embodies the pinnacle of human adventure and exploration. While the financial and procedural barriers are significant, the allure of making history and witnessing the Earth rise from the lunar horizon is, for some, worth every penny and every step in the preparation process. With this understanding of what to expect, both financially and procedurally, your lunar dream is closer to reality.
Space Mission Cost Analysis Report
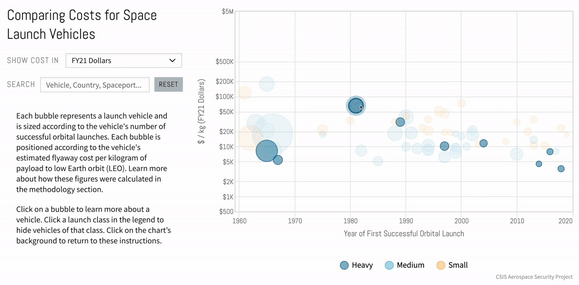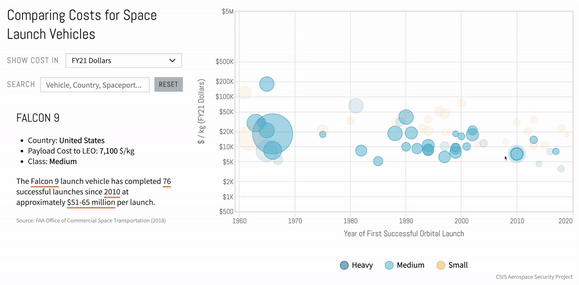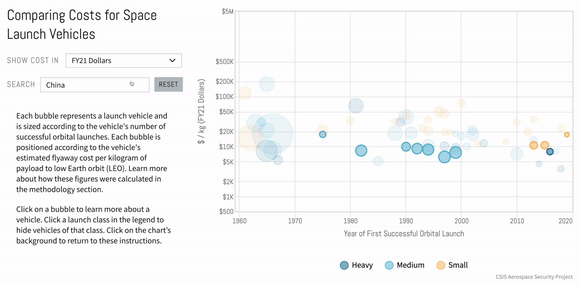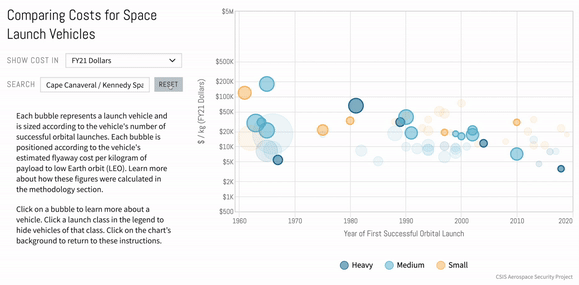
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving domain of space exploration, the economic aspect of conducting missions has garnered significant attention. As ambitions soar, so do the costs associated with spacecraft development, launch operations, astronaut training, and ensuring mission safety. This cost analysis aims to dissect these major cost components, identifying opportunities for optimization to enhance cost efficiency while accurately forecasting budget requirements, in line with the overarching goals of maintaining mission integrity and safety.
Major Cost Components
1. Spacecraft Development
Development costs encompass the design, engineering, testing, and manufacturing of spacecraft. This represents a substantial portion of the mission’s total expenses due to the complex technology and specialized materials required.
Optimization Strategies:
- Reusable Spacecraft: Evaluating the feasibility and potential savings from utilizing reusable spacecraft systems to reduce the need for new builds.
- Adoption of Best Practices: Leveraging learnings from past missions to streamline development processes.
2. Launch Expenses
The costs associated with launching a spacecraft into space are another significant contributor. This includes the use of launch vehicles, fuel, launch pad maintenance, and associated personnel.
Optimization Strategies:
- Shared Launch Platforms: Exploring opportunities to share launch services with other entities to distribute the fixed costs associated with launch operations.
- Alternative Launch Technologies: Investigating newer, cost-effective launch technologies that could potentially lower expenses.
3. Astronaut Training
Training astronauts is an intensive and costly process, involving simulators, safety drills, and mission-specific preparation.
Optimization Strategies:
- Streamline Training Programs: Reviewing current programs to identify and eliminate redundancies, focusing on efficiency without compromising mission readiness.
- Enhanced Simulation Technologies: Investing in advanced simulation technologies to reduce the need for expensive real-world training scenarios.
4. Safety Measures
Ensuring the safety of astronauts and mission success involves rigorous testing, the development of fail-safes, and emergency protocols which add to the mission cost.
Optimization Strategies:
- Cost-effective Safety Technologies: Incorporating advanced yet affordable safety systems and technologies to protect crew and spacecraft without exorbitant costs.
- Automation: Assessing areas where automated systems can safeguard mission integrity, thereby reducing the reliance on costly manual oversight and intervention.
Areas for Cost Optimization and Efficiency Improvement
By focusing on reusable spacecraft, the investment in development can be significantly reduced over multiple missions. Shared and alternative launch platforms present a viable strategy for lowering launch expenses by spreading costs across various users and taking advantage of emerging technologies.
In astronaut training programs, streamlining and adopting high-fidelity simulation technologies can achieve substantial savings. This approach not only reduces direct costs but also enhances training effectiveness by closely mimicking real-world scenarios.
Integrating cost-effective safety measures and leveraging automation wherever possible can ensure high safety standards are maintained without disproportionately inflating the mission budget. Furthermore, a continual assessment and adoption of best practices from past missions offer ongoing opportunities for cost savings and efficiency gains.
Conclusion
This analysis underscores the multifaceted nature of cost components in space missions, highlighting significant opportunities for optimization across spacecraft development, launch operations, astronaut training, and safety measures. By strategically implementing the outlined optimization strategies, it is feasible to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and maintain the safety and integrity of space missions. This proactive approach to cost management and efficiency will be crucial as space agencies and private entities alike strive to advance their capabilities and reach in the new era of space exploration.
Lunar Mission Costs: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
The allure of the Moon has captivated humanity for centuries, leading to significant advancements in space exploration. However, the financial aspect of reaching the lunar surface is a topic of great interest and discussion. This analysis aims to compare the costs associated with modern commercial lunar missions with those of historical government-funded endeavors, shedding light on the economic impacts of these monumental projects.

Modern Commercial Lunar Missions
1. SpaceX’s Planned Lunar Mission
SpaceX, a pioneer in commercial spaceflight, announced a planned mission to send Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa and a group of artists around the Moon aboard the Starship spacecraft, at an estimated cost of over $2 billion. This mission, known as #dearMoon, signifies a major leap towards commercial lunar tourism.
2. NASA’s Artemis Program
While NASA’s Artemis program is primarily a government-led initiative, it heavily relies on partnerships with private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin. The program aims to return humans to the Moon by 2024, with a total estimated cost of around $35 billion. This collaboration highlights the evolving relationship between public and private sectors in space exploration.
3. Blue Origin’s Blue Moon Lander
Blue Origin’s proposed Blue Moon lunar lander, with an estimated cost of between $5 billion and $10 billion over five years, represents a major investment in establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon.
4. NASA Contracts for Lunar Landing Systems
In 2020, NASA awarded contracts totaling $967 million to SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Dynetics for the development of human lunar landing systems. This step aims to reduce the overall cost of lunar exploration by leveraging commercial innovation.
Historical Government-Funded Lunar Missions
Apollo Program
The Apollo Program, which achieved the first human landing on the Moon in 1969, had a total cost of $25.4 billion in 1973 dollars, equivalent to about $150 billion today. This colossal investment by NASA paved the way for future space exploration, setting a high benchmark in terms of financial commitment and technological achievement.
Soviet Union’s Lunokhod Program
The Lunokhod program, characterized by deploying remote-controlled rovers to the Moon, was part of the Soviet Union’s broader lunar exploration efforts. The program’s expenses exceeded $4 billion in 1973 dollars, roughly equating to $20 billion today, showcasing the significant financial undertaking by the Soviet Union in the space race.
Post-Apollo Missions and the Space Race
Post-Apollo missions, including the Apollo Applications Program like Skylab, cost around $10 billion between 1971 and 1974, amounting to approximately $60 billion in today’s dollars. Overall, the Space Race, a direct competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, incurred costs exceeding several hundred billion dollars adjusted for inflation, highlighting the enormous financial and economic stakes involved.
Economic Impact
Modern commercial lunar missions promise to stimulate technological advancements, creating new industries and job opportunities while fostering economic growth. The collaboration between private and public sectors can enhance the efficiency and feasibility of space exploration, potentially making space travel more accessible.
Historical government-funded missions, such as the Apollo program, not only showcased the potential for large-scale projects to drive technological innovation but also inspired a generation of scientists and engineers. The long-term benefits of these missions have been substantial, contributing to global economic growth and technological advancement.
Comparing the costs of modern commercial lunar missions to historical government-funded ones underscores the shifting dynamics of space exploration. The entrance of private companies into the space sector signifies a new era of innovation and collaboration, promising to reduce the costs and increase the frequency of lunar exploration. While the financial investments remain significant, the potential economic and societal benefits of returning to the Moon could well outweigh the costs, heralding a new frontier in human achievement and progress.
Current Accessibility to Moon Trips / Discuss whether these trips are accessible only to the ultra-wealthy or if there are prospects for wider accessibility in the future.
Luxury travel has always been a hallmark of opulence, offering experiences that are as remarkable in their execution as they are exclusive in their clientele. Today’s pinnacle of lavish travel spans luxury yacht cruises, private jet vacations, exclusive resort stays, bespoke safari adventures, and the nascent industry of lunar travel. While these premium experiences exemplify the heights of human ingenuity and the natural world’s wonders, they have traditionally been accessible only to a select few. However, the question arises: as we look to the future, could these extraordinary travel options become more widely available?
Factors Contributing to High Costs
- Technology and Development: Space travel demands cutting-edge technology and rigorous testing to ensure safety, which involves substantial financial investment.
- Risk Management: The inherent risks of space travel necessitate expensive insurance and high-end safety protocols.
- Limited Infrastructure: Unlike commercial aviation, which has widespread infrastructure, space travel lacks established routes and systems, increasing its rarity and price.
Prospects for Wider Accessibility in the Future
- Technological Advances: As aerospace technology evolves and becomes more efficient, the costs of spacecraft production, fuel, and maintenance may decrease. Reusable launch vehicles, for example, have already begun to reduce the cost of sending payloads into orbit.
- Increased Competition: As more companies enter the space tourism market, increased competition might drive down prices. This has been observed in the early days of commercial air travel, which was initially a luxury but became accessible to the general public as more players entered the market.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments and private space companies could subsidize costs for research and development. Such partnerships might also aim at democratizing space travel to ensure broader access.
- Economic Scaling: As operations scale, the economics of larger production can distribute fixed costs over more flights, potentially lowering ticket prices.
- Potential Market Growth: With growing interest in space tourism, there might be market pressure to make space travel more affordable to middle-income earners, not just the ultra-wealthy.
Challenges to Wider Accessibility
- Safety and Regulation: Ensuring passenger safety in space is far more complex than on Earth. Regulatory hurdles will also increase costs.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of increasing space launches could lead to regulatory and operational challenges that might also influence cost.
- Economic Barriers: Despite decreasing costs, space travel is likely to remain an expensive endeavor, given the high technology and safety standards required.
Current State of Luxury Travel Accessibility
At present, the ultra-wealthy predominantly enjoy high-caliber travel experiences. There are several key factors influencing this dynamic:
- High Costs: The substantial financial outlay necessary for luxury travel, from custom travel packages to private space flights, inherently limits access.
- Limited Availability: The exclusivity and bespoke nature of these offerings ensure that only a select number of participants can engage, maintaining a sense of rarity.
- Geographical and Infrastructural Limitations: Many luxurious experiences are set in remote or specially curated environments, demanding infrastructure that supports exclusivity.
- Brand Positioning: The luxury travel market often differentiates itself through exclusivity, reinforcing the barrier to widespread access.
Yet, amidst these constraints lies potential for change, driven by technological advancements, market forces, and evolving consumer values.
Pathways to Wider Accessibility

Technological Innovation
Innovations in transportation, lodging, and service provision could significantly reduce costs and improve efficiency. In the realm of space tourism, for example, reusable rockets and advancements in aerospace engineering are gradually reducing the prohibitive expense associated with leaving Earth’s atmosphere.
Market Competition and Scale
An increase in service providers within the luxury travel sector introduces competition, which can lead to more favorable pricing and package options for consumers. Similarly, as services scale, the fixed costs of operation distribute over a larger base, potentially lowering individual participation costs.
Value of Experiences Over Possessions
A shifting consumer mindset that prioritizes unique experiences over material goods may prompt luxury travel providers to broaden their market appeal. By offering a range of options catering to this desire, companies can maintain exclusivity while inviting a more diverse clientele.
Democratic Space Exploration
With lunar travel, the cooperation between governments and private sectors, aiming to democratize access to space, signifies a future where trips beyond our planet could be within reach for many more individuals. Education, research, and public interest initiatives may also play a role in making outer space a common human domain.
Challenges to Overcome
Despite the optimism, there are hurdles on the path to making luxury travel more accessible:
- Ensuring Safety and Compliance: High-standard safety protocols in extreme or novel environments (like space) will remain costly.
- Environmental Sustainability: Addressing the ecological impact of increased travel, especially in pristine or fragile ecosystems, is paramount.
- Economic Feasibility: Even with cost reductions, the inherent expense of quality, safety, and exclusivity means luxury travel will likely remain a significant investment.
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Future
Luxury travel experiences, whether sailing the high seas on a lavish yacht or stepping foot on the lunar surface, encapsulate human ambition and the desire for discovery. While currently reserved for the affluent, the trajectory of technology, alongside shifts in market dynamics and consumer values, points towards a future where such exquisite journeys may be accessible to a broader audience. However, realizing this future demands overcoming substantive challenges, particularly around sustainability, safety, and affordability. Yet, if the past century’s rapid evolution of travel has taught us anything, it’s that barriers once deemed insurmountable can eventually be transcended.
Economic Impact of Lunar Tourism
Lunar tourism represents a frontier not just in human exploration but also in the expansion of economic horizons. This nascent industry, still in its embryonic stages, holds promise for profound impacts on Earth’s economy, and possibly on space habitats in the future. Here, we explore the various economic factors at play, provide insights on the potential evolution of lunar tourism, and discuss the economic models that can be applied to analyze its impacts.
Economic Factors to Consider
Space Infrastructure
The development of space infrastructure is a critical economic factor. This includes the technology and facilities necessary for lunar travel—rockets, lunar landers, space stations, and habitats on the moon itself. The investment required for these projects is immense, but it’s an investment that could spur significant economic activity. Construction, innovation, and maintenance of space infrastructure could drive job creation and stimulate industries related to aerospace, engineering, and technology.
Tourism Revenue
Initially, lunar tourism is likely to cater to a niche market of affluent individuals, given the high costs associated with space travel. This exclusivity means significant revenue for companies that break into the space tourism industry early. However, as technological advancements lower costs, a broader tourist base could emerge. This expansion would not only increase tourism revenue but also fuel a wider range of economic activities related to travel, such as hospitality services on the moon, training for lunar tourists, and specialized equipment manufacturing.
Exploring New Frontiers: The Economic Impact of Lunar Tourism on Earth and Space Economies
| Aspect | Impact on Earth’s Economy | Impact on Space Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Investment & Development | Increased investment in aerospace sectors, leading to job creation and technological advancements. | Infusion of capital and resources to establish and expand space-based infrastructure and habitats. |
| Tourism Revenue | Enhanced revenue for companies involved in space tourism, potentially contributing to national GDPs. | Generation of a new economic sector entirely based in space, providing services and experiences. |
| Technological Spin-offs | Innovations developed for space travel can be adapted for use in other industries, boosting economic growth. | Accelerated technological advancements necessary for living and working in space. |
| Employment | Creation of high-skilled jobs in aerospace, engineering, and related sectors. | Opportunities for new careers in space, from pilots and engineers to hospitality and support services. |
| Regulatory Frameworks | Development of new laws and regulations to manage space travel, requiring new governance structures. | Establishment of legal and economic systems to govern transactions, property rights, and more in space. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential negative impacts due to increased launches, necessitating new environmental policies and measures. | Challenges in waste management and sustainable living, driving innovation in environmental technologies. |
| Education and Training | Growth in educational programs focusing on aerospace and related fields, enhancing skill development. | Development of specialized training programs tailored to life and work in space environments. |
Future Predictions and Economic Impact
Predictions about lunar tourism’s development hinge on both technological advances and economic viability. In the short to medium term, lunar tourism could function as a luxury market, contributing sizable revenue streams to the pioneering companies. This phase will also see heavy investment in developing the requisite space infrastructure, which itself could be a significant economic driver.
Over time, as access to lunar experiences becomes democratized, the economic impact could broaden. Space habitats might develop their own micro-economies, trading with Earth and among each other. The demand for regular transport between Earth and the moon could feasibly support a robust space transportation industry.
Furthermore, lunar tourism’s need for sustainable solutions—for life support, energy, and food—might catalyze advancements in these domains, with spill-over benefits for Earth’s economy. This could lead to enhanced environmental technologies or more efficient energy solutions being developed for use both on Earth and in space.
Analyzing the Impact with Economic Models
Supply and Demand
The initial supply of lunar tourism opportunities will be low, given the complex infrastructure needed. Coupled with high demand from affluent adventurers, prices are likely to be very high initially. Over time, as supply increases and costs decrease, the market could become more accessible, following a classic supply and demand curve adjustment.
Economic Growth
Investment in space infrastructure and subsequent revenues from lunar tourism could contribute to economic growth. This can be analyzed through models that consider multi-sector impacts, including direct employment in aerospace and related sectors, as well as indirect growth through technological advancement and increased global spending capacity.
Game Theory
Game theory can be applied to understand the strategic interactions between different countries and companies competing in the lunar tourism sector. It can analyze how cooperation and competition might shape the industry’s development, pricing strategies, and international agreements on space travel and lunar activities.
Lunar tourism has the potential to become a significant economic force, driving innovation, creating new job categories, and even fostering the development of new economic sectors related to space exploration. While the industry is still in its infancy, its long-term prospects offer exciting possibilities for economic expansion, both on Earth and, potentially, in space. The interplay between technological advancements and economic models will be key to understanding and maximizing the benefits of this new frontier.

