Understanding the parts of a telescope is essential for both beginners and seasoned astronomers. A telescope is a complex instrument designed to magnify distant objects, allowing us to explore the universe in greater detail. In this article, we will delve into the various components that make up a telescope, explaining their functions and importance in astronomical observation.
Parts of a telescope: Main Components of a Telescope
Objective Lens or Mirror

The objective lens or mirror is the primary optical element of a telescope, responsible for gathering and focusing light. In refractor telescopes, this component is a lens, while in reflector telescopes, it is a mirror.
- Refractor Telescopes: Use a large objective lens at the front of the telescope to bend and focus light.
- Reflector Telescopes: Utilize a concave primary mirror at the base of the telescope tube to reflect and focus light onto a secondary mirror.
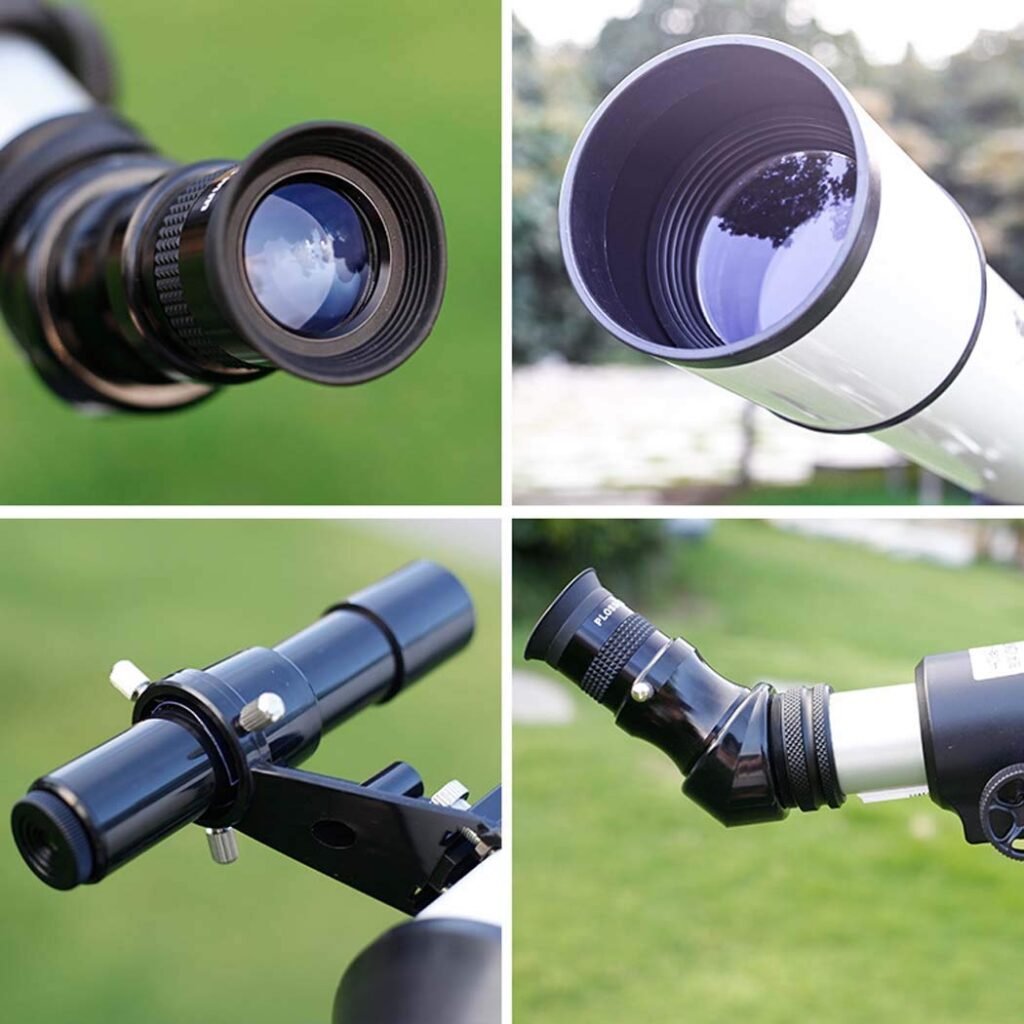
Eyepiece
The eyepiece is the part of the telescope through which you look. It magnifies the image formed by the objective lens or mirror. Eyepieces come in various focal lengths, affecting the magnification and field of view.
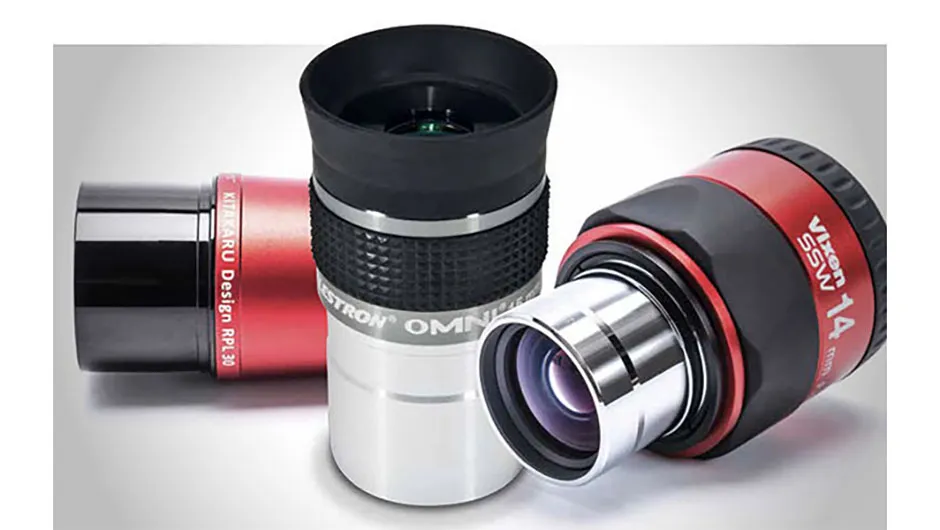

- Focal Length: Shorter focal length eyepieces provide higher magnification but a narrower field of view, while longer focal lengths offer lower magnification and a wider field of view.
- Types of Eyepieces: Common types include Plössl, Orthoscopic, and Wide-Angle eyepieces, each offering different viewing experiences.
Focuser
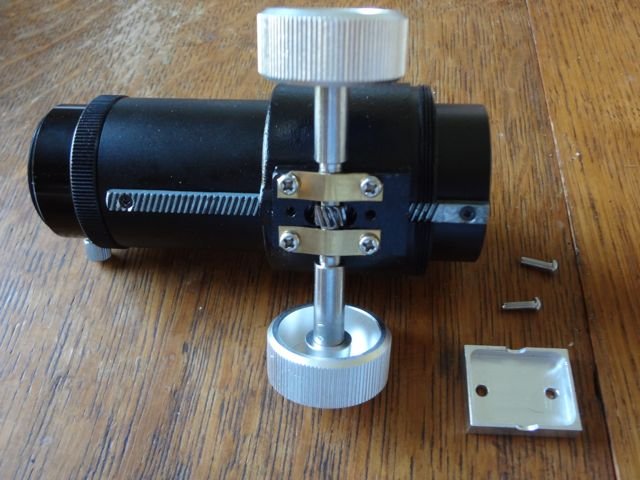


The focuser is a mechanism that allows precise adjustment of the telescope’s focus. It moves the eyepiece closer to or farther from the objective lens or mirror, bringing the observed object into sharp focus.
- Rack and Pinion Focuser: Uses a geared track to move the eyepiece smoothly.
- Crayford Focuser: Offers more precision and less backlash compared to rack and pinion focusers.
Finderscope
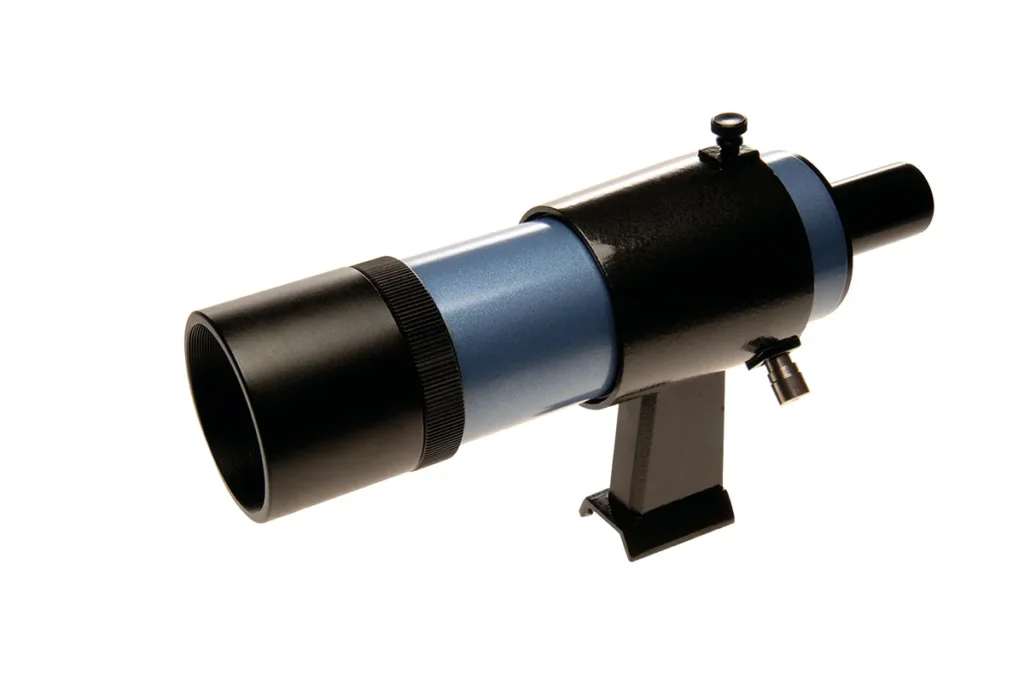

A finderscope is a small auxiliary telescope mounted on the main telescope. It provides a wider field of view, making it easier to locate celestial objects before observing them through the main telescope.
- Red Dot Finders: Project a red dot onto a lens, helping align the telescope with the desired object.
- Optical Finders: Use a crosshair to help aim the telescope.
Mount
The mount is a crucial part of the telescope that supports and stabilizes it. It allows smooth movement and accurate tracking of celestial objects.
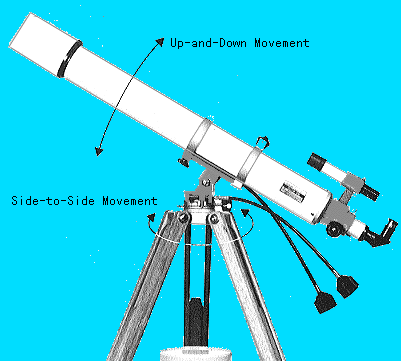
- Altazimuth Mount: Moves the telescope in altitude (up and down) and azimuth (side to side), ideal for beginners due to its simplicity.
- Equatorial Mount: Aligns with Earth‘s axis, enabling precise tracking of celestial objects as they move across the sky. Suitable for advanced users and astrophotography.
Tripod or Pier

The tripod or pier provides a stable base for the telescope and mount. It is essential for reducing vibrations and ensuring steady observations.
- Tripods: Typically made of aluminum or steel, offering portability and ease of setup.
- Piers: More stable and permanent, often used in observatories.
Additional Components
Diagonal Mirror or Prism

A diagonal mirror or prism is used in refractor and compound telescopes to redirect the light path, providing a more comfortable viewing angle. It reflects the light by 90 degrees, allowing for easier observation of objects high in the sky.
- Star Diagonals: Used for astronomical observations.
- Correct-Image Diagonals: Provide an upright image, useful for terrestrial viewing.
Barlow Lens


A Barlow lens is an accessory that increases the effective focal length of the telescope, thereby increasing magnification. It is inserted between the eyepiece and the focuser.
- 2x Barlow Lens: Doubles the magnification.
- 3x Barlow Lens: Triples the magnification.
Filters
Filters are used to enhance contrast, reduce glare, and protect the eyes during specific observations. They come in various types, each serving a different purpose.

- Color Filters: Enhance details of planets and the Moon.
- Solar Filters: Allow safe observation of the Sun.
- Light Pollution Filters: Improve visibility of celestial objects in light-polluted areas.
GoTo Systems
GoTo systems are computerized mounts that automatically locate and track celestial objects. These systems are particularly useful for beginners and those interested in astrophotography.
- Database: Includes thousands of celestial objects, accessible at the push of a button.
- Tracking: Automatically tracks objects as they move across the sky, maintaining them in the field of view.
Tube Rings and Dovetail Plates
Tube rings and dovetail plates are used to secure the optical tube to the mount. They provide a stable connection and allow for easy adjustments and balancing of the telescope.
- Tube Rings: Clamp around the optical tube and attach to the dovetail plate.
- Dovetail Plates: Slide into the mount’s dovetail saddle, providing a quick-release mechanism.
Understanding the parts of a telescope is fundamental for maximizing your observational experience. From the primary objective lens or mirror to the eyepiece, focuser, and mount, each component plays a vital role in the telescope’s performance. Additional accessories like finderscopes, filters, and GoTo systems enhance functionality and ease of use. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you can make informed decisions when choosing and using a telescope, ensuring a rewarding journey through the cosmos.

